Biodegradable floating hydrogel baits as larvicide delivery systems against mosquitoes†
Abstract
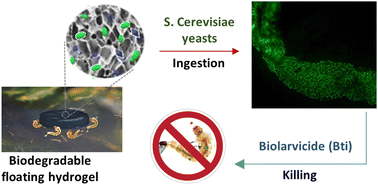
Biological methods for mosquito larvae control are completely biodegradable and have null or limited effects on nontarget organisms. However, commercially available products have a low residual activity, with the consequent need for multiple applications that inevitably increase costs and the risk of resistance phenomena insurgence. Smart delivery systems made of hydrogels proved their efficacy in increasing the action duration of biolarvicides up to several months, but the lack of an efficient baiting mechanism to strongly attract the target pest remains a problem in practical applications. In this work, we investigated two novel hydrogel-based formulations of completely natural composition for baiting and killing larvae of Aedes albopictus mosquitos. The proposed materials consist of charged crosslinked polysaccharides (chitosan and cellulose) and are specifically manufactured to float in water, simulating organic matter usually present at breeding sites. Within the hydrogels’ matrix, yeast colonies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae were embedded as phagostimulants alongside a biolarvicide (Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis (Bti)). Despite the similar chemical nature and structure, chitosan-based hydrogels exhibited a markedly superior baiting potential compared to those made of cellulose and also succeeded in efficiently killing mosquito larvae just after a few hours from administration. We are confident that the proposed smart delivery hydrogel made of chitosan can be an enabling tool to attract mosquito larvae towards biopesticides of different nature without delocalizing active ingredients away from the breeding site and to simultaneously increase their residual activity, thus holding the potential of minimizing environmental pollution related to pest control and vector-borne disease prevention.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...