Ag/AgCl clusters derived from AgCu alloy nanoparticles as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
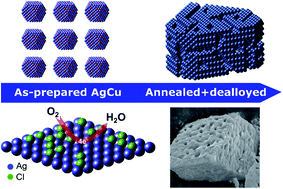
The structural changes induced by the selective dealloying of bimetallic alloy electrocatalysts could have a significant impact on the kinetics of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Herein, we show that the activity of bimetallic AgCu alloy nanoparticles (NPs) towards the ORR can be enhanced by dealloying Cu in an acidic medium. A combination of core-level X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction investigations with scanning electron microscopy reveals that dealloying in HCl performed on annealed AgCu alloy NPs leads to the formation of relatively large nanostructures composed of Ag/AgCl. The initial composition of AgCu alloy NPs and the extent of the AgCl formation on Ag surfaces have a significant effect on the ORR activity. Furthermore, the formation of the active surface structure strongly depends on the initial composition of alloy NPs. Ag decorated with AgCl formed after dealloying Ag7Cu3 alloy NPs presents a superb ORR activity with a high onset potential (E0) of ≈0.97 V vs. RHE, comparable to commercial Pt/C catalysts and outperforms dealloyed Ag3Cu2 and pristine Ag electrocatalysts. We suggest that Ag+ stabilized in the presence of sub-stoichiometric Cl− plays a critical role in the superior activity of the catalyst.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...