A sustainable strategy for spent Li-ion battery regeneration: microwave-hydrothermal relithiation complemented with anode-revived graphene to construct a LiFePO4/MWrGO cathode material†
Abstract
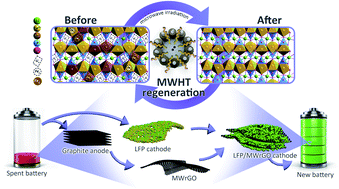
With the upcoming retirement of widely employed LiFePO4 (LFP) batteries, a sustainable strategy for recycling their valuable components is urgent. In this work, spent LFP cathodes were revived through a microwave-hydrothermal relithiation process, complemented with microwave-reduced graphene oxide (MWrGO) derived from spent graphite anodes, to form a composite LFP/MWrGO cathode material. The defect–repair process, performed under optimal conditions (150 °C for 1 h), allows LFP cathodes to gain better morphology and electrochemical performance with a specific capacity of 150.5 mA h g−1 at 0.1C. The introduction of anode-revived graphene via electrostatic self-assembly helps form a hierarchical structure and conductive network for regenerated LFP, enabling fast ion and electron transfer for redox reactions. When doped with 5 wt% graphene, the regenerated LFP/MWrGO composite displays an enhanced specific capacity of 161.4 mA h g−1 and high capacity retention (i.e., 94.9% over 100 cycles) at 0.2C. Laboratory-scale economic and environmental analyses indicate that the entire regeneration process has a favorable atom economy of recovery with low energy/time/reagent consumption and greenhouse gas emission, owing to the featured microwave-material interaction. This study provides a green facile method as a reference for the regeneration of spent LFP batteries, which can be extended to other types of batteries, and promotes the sustainability of Li-ion battery downstream technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...