The co-adsorption of thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (THQ) and coumarin present in the aqueous extract of Ayapana triplinervis on mild steel and its protection in hydrochloric acid up to 323 K: computational and physicochemical studies
Abstract
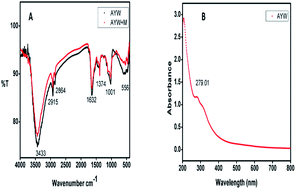
This study evaluates the corrosion inhibition property of the aqueous and alcoholic leaf extracts of the medicinal plant Ayapana triplinervis. The major components in the extracts are thymohydroquinone dimethyl ether (THQ) and coumarin. It is clear from the weight-loss studies that the water extract of the leaves (AYW) is superior to the alcoholic extract (AYA) in terms of offering corrosion inhibition. The 96% efficiency of 4% (v/v) AYW in 0.5 N HCl at room temperature changes to 84.62% at 323 K. The mixed-type inhibition behaviour of AYW shows slight dominance in the anodic direction. Studies suggest the multilayer adsorption of phytochemicals on the metal surface and that the adsorption follows the Temkin model. Theoretical studies using DFT and BIOVIA Materials Studio investigations establish THQ as a good inhibitor with high adsorption characteristics. Even though the concentration of coumarin in the extract is low, its presence in the extract facilitates the adsorption of THQ on the metal surface, which is evident from the MD simulation study. The changes in the surface topography and elemental composition of the metal specimen in the inhibited and uninhibited solution are monitored by SEM and EDX spectral studies. XPS data support the presence of both THQ and coumarin on the metal surface and the existence of co-ordinate bonding between the metal's d orbital and the O atoms of THQ. Theoretical and experimental studies support the mixed mode of adsorption of THQ as physisorption followed by chemisorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...