Natural parsley oil as a green and safe inhibitor for corrosion of X80 carbon steel in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution: a chemical, electrochemical, DFT and MC simulation approach
Abstract
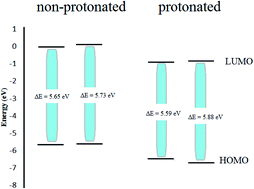
This work focuses on the use of natural parsley oil as a safe, eco-friendly and cost-effective inhibitor for dissolution of X80 carbon steel (X80CS) in 0.5 M H2SO4 solution. Electrochemical and chemical measurements and theoretical studies were utilized to determine the inhibitory vigor of parsley oil. The inhibition efficacy increases with an increase in the parsley oil concentration and a decrease in temperature. It reached 95.68% at 450 ppm of parsley oil. The inhibition process is explained by spontaneous adsorption of the oil on the X80CS. Adsorption is described by the Langmuir isotherm model. The polarization data demonstrate that parsley oil is categorized as a mixed inhibitor with a dominant control of the cathodic reaction. Parsley oil inhibits the pitting corrosion of X80CS in the presence of NaCl solution by moving the pitting potential to a more positive mode indicating protection against pitting attack. The thermodynamic parameters for activation and adsorption were computed and interpreted. The four chemical components in natural parsley oil were examined using density functional theory (DFT). Monte Carlo (MC) simulation was performed to study the adsorption of parsley oil on the X80CS surface. The outcomes confirmed that the Apiole molecule is the most effective in the inhibition process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...