Anaerobic self-assembly of a regenerable bacteria-quantum dot hybrid for solar hydrogen production†
Abstract
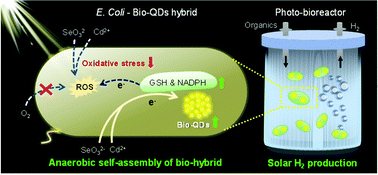
Inorganic–biological hybrid systems (bio-hybrids), comprising fermentative bacteria and inorganic semiconductor photosensitizers for synergistic utilization of solar energy and organic wastes, offer opportunities for sustainable fuel biosynthesis, but the low quantum efficiency, photosensitizer biotoxicity and inability for self-regeneration are remaining hurdles to practical application. Here, we unveil a previously neglected role of oxygen in suppressing the biosynthesis of cadmium selenide quantum dots (CdSe QDs) and the metabolic activities of Escherichia coli, and accordingly propose a simple oxygen-regulation strategy to enable the self-assembly of bacterial–QD hybrids for efficient solar hydrogen production. Shifting from aerobic to anaerobic biosynthesis significantly lowered the intracellular reactive oxygen species level and increased NADPH and thiol-protein production, enabling a two-order-of-magnitude higher bio-QD synthesis rate and resulting in CdSe-rich products. Bacteria with abundant biocompatible intracellular bio-QDs naturally formed a highly active and self-regenerable bio-hybrid and achieved a quantum efficiency of 28.7% for hydrogen production under visible light, outperforming all the existing bio-hybrids. It also exhibited high stability during cyclic operation and robust performance for treating real wastewater under simulated sunlight. Our work provides valuable new insights into the metallic nanomaterial biosynthesis process to guide the design of self-assembled bio-hybrids towards sustainable energy and environmental applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...