Deciphering pathological remodelling of the human cartilage extracellular matrix in osteoarthritis at the supramolecular level†
Abstract
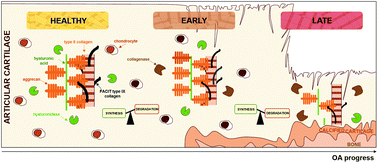
The extracellular matrix (ECM) of articular cartilage is a three-dimensional network mainly constituted of entangled collagen fibrils and interfibrillar aggrecan aggregates. During the development of osteoarthritis (OA), the most common musculoskeletal disorder, the ECM is subjected to a combination of chemical and structural changes that play a pivotal role in the initiation and the progress of the disease. While the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathological remodelling of the ECM are considered as decisive, they remain, however, not completely elucidated. Herein, we report a relevant way for unravelling the role and nature of OA progress on human cartilage tissues, in terms of chemical composition and morphological and mechanical properties at the level of supramolecular assemblies constituting the cartilage ECM. For this purpose, we used X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and developed an innovative methodological approach that provides the molecular composition of the ECM. Moreover, we used atomic force microscopy (AFM) to probe the tissues at the level of individual collagen fibrils, both imaging and force spectroscopy modes being explored to this end. Taken together, these nanoscale characterization studies reveal the existence of two stages in the OA progress. At the early stage, a marked increase in the aggrecan and collagen content is observed, reflecting the homeostatic chondrocyte activity that tends to repair the cartilage ECM. At the late stage, we observe a failed attempt to stabilize and/or restore the tissue, yielding significant degradation of the supramolecular assemblies. This suggests an imbalance in the chondrocyte activity that turns in favor of catabolic events. Chemical changes are also accompanied by ECM structural changes and stiffening. Interestingly, we showed the possibility to mimic the imbalanced activities of chondrocytes by applying enzymatic digestions of healthy cartilage, through the combined action of hyaluronidase and collagenase. This yields damage strictly analogous to that observed at high OA severity. These findings bring mechanistic insights leading to a better understanding of the mechanism by which OA is initiated and progresses in the cartilage ECM. They offer guidelines for the development of curative treatments, such as targeting the homeostatic balance of chondrocyte metabolism through the control of enzymatic reactions involved in catabolic processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...