Opposite effects of gold and silver nanoparticle decoration of graphenic surfaces on bacterial attachment†
Abstract
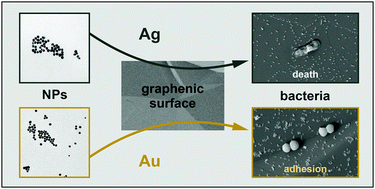
The interaction between bacteria and nanoparticles is currently a central topic in bionanotechnology. In this work, we investigated how the deposition of two kinds of metallic (Au and Ag) nanoparticles (AuNPs and AgNPs, respectively, ∼25 nm) on model graphenic surfaces affects bacterial attachment and survival. The nanoscale functionalization of the graphenic surface resulted in bacterial attachment (AuNPs) and bactericidal effects (AgNPs). The observed tendencies provide general insight into bacteria/nanoparticle/surface interactions, because they were observed for both Gram-negative (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis) bacterial strains. Interestingly, the simultaneous deposition of AuNPs and AgNPs served two functions at the same time, enhancing both bacterial attachment and antibacterial potential. The antibacterial properties of the AgNPs were explained in terms of electronic effects. Their deposition on graphene led to a decrease in the work function, promoting electron transfer to dioxygen molecules, and formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that react with the walls of bacterial cells and effectively destroy them. This work provides useful insight for the design and development of graphenic surfaces, for which tuning the interactions (attraction/repulsion and bacteriostatic/bactericidal effects) at the carbon material–microorganism interface represents an essential task.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...