Recyclable carbon nanotube/silicone oil emulsion with NaOH aqueous solution for indoor CO2 capture†
Abstract
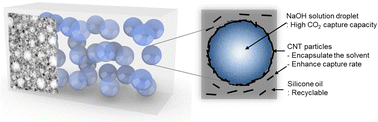
Emulsion solvents (ES), which are liquid absorbent-based CO2 capture materials, are developed as simple and expandable droplets to control CO2 capture performance. An aqueous NaOH solution, which is a chemical absorbent, is encapsulated by functionalized carbon nanotubes (CNTs) to form a solid adsorbent by enhancing the high lipophilicity and high-viscosity silicone oil. The ratio of each component controls the CO2 capture performance of the solvent. It is shown that droplets of NaOH aqueous solution formed in fine sizes improve the efficiency of the chemical reaction capacity of NaOH and CO2, and thus, even when crystallization occurs, they can be used in a stationary environment, and NaOH can be used at a high concentration. It is found that the optimum concentration of CNTs required to minimize the size of the emulsion is 0.075 wt%, while the CO2 capture capacity is 2.23 mmolCO2 g−1ES–NaOH at a pure CO2 concentration and 1.31 mmolCO2 g−1ES–NaOH at a low CO2 concentration (2000 ppm, 50% relative humidity). The oil phase can be recycled continuously by separating the crystallized aqueous phase after the CO2 capture. These results demonstrate that chemical absorbents with excellent CO2 capture performance can be used safely and for a long time in order to reduce indoor CO2, and the CO2 capture performance can be flexibly controlled.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...