Digestion characteristics of quinoa, barley and mungbean proteins and the effects of their simulated gastrointestinal digests on CCK secretion in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells
Abstract
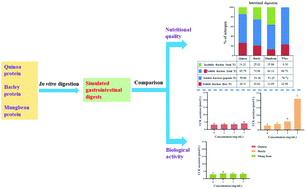
The demand for plant-based proteins has been rapidly increasing due to sustainability, ethical and health reasons. The present study aimed to investigate the digestion characteristics of three plant proteins (quinoa, barley and mungbean) based on an in vitro digestion model and the effect of their simulated gastrointestinal digests on satiety hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) secretion in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. The nitrogen distribution in the digestion process, the relative molecular weight (MW) of peptides and the amino acid composition in simulated gastrointestinal digests were characterized. Quinoa protein had the highest proportion of soluble nitrogen after gastrointestinal digestion (85.79%), followed by barley protein (74.98%) and mungbean protein (64.14%), suggesting that quinoa protein was more easily digested than barley and mungbean proteins. The peptides but not free amino acids were the main components in the gastrointestinal digests of quinoa, barley, and mungbean proteins. The gastrointestinal digest of quinoa protein had a well balanced amino acid pattern, whereas that of barley protein was lacking Lys, and that of the mungbean protein was short of sulfur amino acids (Phe + Tyr) but rich in Lys. In terms of the ability to stimulate CCK secretion, the gastrointestinal digest of barley protein had a strong stimulatory effect on CCK secretion, while that of quinoa and mungbean proteins had only a weak stimulatory effect. After pretreatment with a specific calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) antagonist NPS 2143, CCK secretion induced by the barley protein digest was greatly suppressed, indicating that CaSR was involved in barley protein digest-induced CCK secretion. These results show that quinoa protein has good nutritional quality, while barley protein is an excellent plant protein source to stimulate CCK secretion and has a potential application as a dietary supplement for obesity management.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...