Resazurin-based high-throughput screening method for the discovery of dietary phytochemicals to target microbial transformation of l-carnitine into trimethylamine, a gut metabolite associated with cardiovascular disease†
Abstract
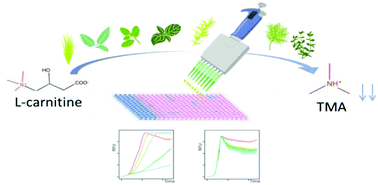
Nowadays, there is great interest in the discovery of food compounds that might inhibit gut microbial TMA production from its methylamine precursors. In this work, an innovative novel screening strategy capable of rapidly determining the differences in the metabolic response of Klebsiella pneumoniae, a bacteria producing TMA under aerobic conditions, to a library of extracts obtained from food and natural sources was developed. The proposed high-throughput screening (HTS) method combines resazurin reduction assay in 384-well plates and Gaussian Processes as a machine learning tool for data processing, allowing for a fast, cheap and highly standardized evaluation of any interfering effect of a given compound or extract on the microbial metabolism sustained by L-carnitine utilization. As a proof-of-concept of this strategy, a pilot screening of 39 extracts and 6 pure compounds was performed to search for potential candidates that could inhibit in vitro TMA formation from L-carnitine. Among all the extracts tested, three of them were selected as candidates to interfere with TMA formation. Subsequent in vitro assays confirmed the potential of oregano and red thyme hexane extracts (at 1 mg mL−1) to inhibit TMA formation in bacterial lysates. In such in vitro assay, the red thyme extract exerted comparable effects on TMA reduction (∼40%) as 7.5 mM meldonium (∼50% TMA decrease), a reported L-carnitine analogue. Our results show that metabolic activity could be used as a proxy of the capacity to produce TMA under controlled culture conditions using L-carnitine to sustain metabolism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...