Effects of red raspberry polyphenols and metabolites on the biomarkers of inflammation and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: a pilot study
Abstract
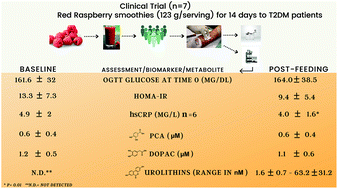
Berry fruits are rich in polyphenolic compounds (PCs) and may promote health benefits. Anthocyanin (ACN) concentrations of red raspberry (RR) (Rubus idaeus) extracts were 887.6 ± 262.8 μg g−1, consisting mainly of cyanidin-3-sophoroside (C3S) equivalents. To test the efficacy of RR in diabetes treatment, seven patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were given one oral RR serving (123 g per day) for two weeks. Blood samples were drawn at the baseline (BSL) and post-feeding (PF) periods for phenolic metabolite, inflammation and insulin resistance (IR) biomarker analysis. Two urolithin conjugates, urolithin A glucuronide (Uro-A glur) and urolithin A sulphate (Uro-A sulf) were identified in the PF period in 5 of the 7 patients in nanomolar concentrations (1.6 ± 0.7–63.2 ± 31.2 nM). ACN-derived metabolites such as protocatechuic acid (PCA) and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) were at micromolar levels and were higher during the PF period for diabetics and the levels were as follows: BSL: PCA = 0.6 ± 0.4, DOPAC = 1.2 ± 0.5; PF: PCA = 0.6 ± 0.4, DOPAC = 1.1 ± 0.6. The results revealed significant reductions in high sensitivity C-reactive protein, hsCRP (p = 0.01) and there was a downward trend in IR measured by the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR, p = 0.0584) in T2DM patients. DOPAC (1–100 μM) failed to stimulate insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. The multiplex assay showed variations in the cytokine levels between patients, but differences were not significant. This study demonstrates a potential use of RR in the treatment of inflammation and possibly IR as well in patients with type 2 diabetes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...