Role of co-existing anions in non-radical and radical processes of carbocatalyzed persulfate activation for acetaminophen degradation†
Abstract
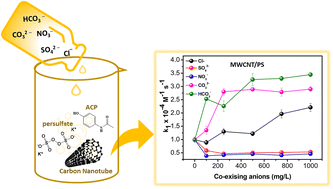
We investigated the effect of co-existing anions of Cl−, SO42−, NO3−, CO32−, and HCO3− on potassium persulfate (PS) activation by multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and N-doped MWCNTs (N-MWCNTs) for acetaminophen (ACP) degradation. The results of radical quenching studies and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) analyses affirmed that non-radical (1O2) and radical (O2˙−, HO˙, and SO4˙−) species initiated the ACP degradation. Catalytic performance studies demonstrated that CO32− and HCO3− provided higher ACP degradation compared to Cl−, SO42−, and NO3−. The observed beneficial and adverse impacts of Cl−, SO42−, and NO3− depend on their concentration. EPR analysis confirms that the radical pathway was modified in the presence of CO32− or HCO3−, which proved that HO˙ and SO4˙− were scavenged by CO32− and HCO3−. Non-radical TEMP–1O2 adduct signals were not changed by co-existing anions, inferring that the high selectivity 1O2 species were resistant to the impact of co-existing anions. An ACP degradation mechanism via electron transfer, acetamide cleavage, mono- and dihydroxylation was proposed based on liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy analysis. The co-existing anions did not noticeably affect the formation of degradation products via the electron transfer mediative pathway, however, Cl−, SO42− and CO32− notably limited the di-hydroxylation pathways.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...