Ceramic membranes with in situ doped iron oxide nanoparticles for enhancement of antifouling characteristics and organic removal†
Abstract
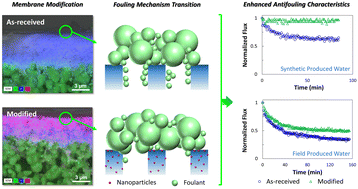
Membrane fouling remains a challenge during the purification of many wastewaters. Here, ceramic membranes were uniformly modified with in situ generated iron oxide nanoparticles (NPs) and applied for the treatment of synthetic and field-produced water (PW). Membrane characteristics, including wettability, fouling/antifouling behavior, and organic rejection were evaluated for different feed types, membrane pore sizes, and NP loadings. Dynamic contact angle and droplet penetration flux revealed increased hydrophilicity not only on the surface but also within the pores of the modified membranes. Decreased roughness and enhanced hydrophilic properties coupled with a more negatively charged surface contributed to improved antifouling characteristics. Flux decline was limited to 6–17%, and fouling reversibility was 80–91%. Analysis of the fouling mechanism showed a transition from standard pore blocking–cake formation to intermediate/complete blocking–cake formation upon modifying the membrane. The modified membranes reduced the organic content of the permeate up to 3 times with a slight flux reduction for the synthetic PW, whereas, in the case of field PW, up to 35% increase in the permeate flux was observed coupled with 6–30% decrease in the permeate organic concentration. Considering the organic rejection, fouling extent, and flux recovery, membrane modification works best at low-NP content and large membrane pore size as reflected by a 40–300% increase in the membrane performance number. Accordingly, optimum NP loading rendered larger pore size membranes to tighter ones while exhibiting a comparable organic rejection, higher permeate flux, and superior antifouling properties. Overall, the results show that the modification technique can be used to enhance the efficacy of new or regenerated ceramic membrane systems for wastewater treatment with minimal cost and no induced damage.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...