Acceptorless dehydrogenation of alcohols to carboxylic acids by palladium nanoparticles supported on NiO: delving into metal–support cooperation in catalysis†
Abstract
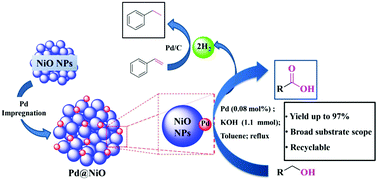
In this work, we have developed a simple NiO-supported Pd nanocatalyst (Pd@NiO) for oxidant-free dehydrogenative oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids along with hydrogen gas as a byproduct. The catalyst has been characterized by techniques like XRD, HRTEM, SEM-EDX, XPS and ICP-AES. The nanostructured Pd@NiO material showed excellent dehydrogenative oxidation activity and outperformed the activity of free NiO or Pd nanoparticles supported on silica/carbon as a catalyst, which could be attributed to synergistic effect of Pd and NiO. A diverse range of aromatic and aliphatic primary alcohols could be efficiently converted to their corresponding carboxylates in high yields with a catalyst loading as low as 0.08 mol%. Notably, highly challenging biomass derived heterocyclic alcohols such as furfuryl alcohol and piperonyl alcohol can also be efficiently converted to their corresponding acids. Moreover, our catalyst can convert benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid on a gram scale with 89% yield. Interestingly, the H2 gas liberated in the reaction can also be used as a substrate for the hydrogenation of 3a to 4a in 65% yield. The nanostructured catalyst is highly reusable and no significant decrease in activity was observed after six reaction cycles. A kinetic study revealed that the reaction followed first-order kinetics with a rate constant of k = 1.47 × 10−4 s−1, under optimized conditions. The extent of reactivity of different functionalities towards dehydrogenation was also investigated using a Hammett plot showing good linearity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...