A novel cyclic dinuclear gold(i) complex induces anticancer activity via an oxidative stress-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in MDA-MB-231 cancer cells†
Abstract
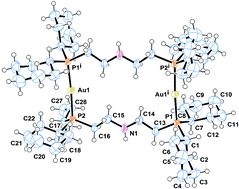
A new dinuclear cyclic gold(I) complex [Au2(DCyPA)2](PF6)2, 1, based on bis[2-(dicyclohexylphosphano)ethyl]amine (DCyPA) has been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis, IR and NMR spectroscopy, and X-ray crystallography. In the dinuclear complex cation [Au2(DCyPA)2]2+, the two gold(I) ions are bridged by the ligand bis[2-(dicyclohexylphosphano)ethyl]amine (DCyPA) giving rise to a 16-membered ring centrosymmetric metallacycle. The cytotoxicity of the complex was evaluated against the triple-negative human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. In order to understand the mechanism of the cytotoxic behavior, a variety of assays, including Annexin V-FITC/Propidium iodide double staining, ROS production, and mitochondrial membrane potential and migration assays were carried out. The results indicated that complex 1 induced cytotoxicity via an oxidative stress-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway in MDA-MB-231 cancer cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...