A mechanistic study of syngas conversion to light olefins over OXZEO bifunctional catalysts: insights into the initial carbon–carbon bond formation on the oxide†
Abstract
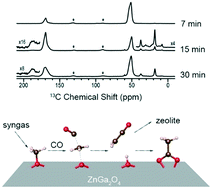
Direct conversion of syngas into light olefins (C2=–C4=) using bifunctional catalysts composed of oxide and zeolite (OXZEO) has attracted extensive attention in both academia and industry. However, the reaction intermediate produced over the oxide surface is still under debate, and direct atomic-level spectroscopic evidence is still lacking. Herein, we choose ZnGa2O4, Ga2O3 and ZnO combined with mordenite (MOR) zeolite as bifunctional catalysts, which show remarkable distinctions in product selectivity. Ex situ NMR detects several C2+ species (acetate, propionate, and isobutyrate) in addition to C1 species on the oxide surface during syngas conversion. Isotope 13C-labeling experiments and DFT calculations reveal that the first carbon–carbon bond may be attributed to ketene forming on the oxide, which can either be transformed into other C2+ species on the oxide surface or diffuse into zeolite for a subsequent reaction. This provides direct spectroscopic evidence for the initial carbon–carbon bond formation on the oxide. The difference in the intermediates on the oxide can account for the difference in product selectivity on OXZEO bifunctional catalysts, in which ketene formation may lead to high selectivity to ethylene.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...