Toward size-dependent thermodynamics of nanoparticles from quantum chemical calculations of small atomic clusters: a case study of (B2O3)n†
Abstract
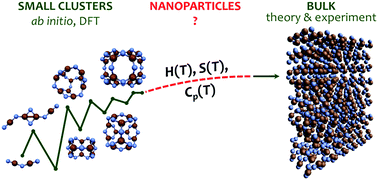
We present a method for obtaining canonical partition functions and, accordingly, temperature-dependent thermodynamics of arbitrary-sized (nano) particles from electronic structure calculations of the corresponding small size atomic clusters. The guiding idea here is to extrapolate the basic properties underlying the thermochemistry of clusters (electronic energies, rotational constants, and vibrational frequencies) rather than the thermodynamic functions themselves. The thus obtained scaling dependences for these basic properties expressed in a simple analytical form provide an efficient tool for fast evaluation of the size-selected thermochemical data for particles of any nuclearity. To exemplify the performance of the methodology, neutral stoichiometric boron oxide clusters are considered. To this end, the geometry and various physical properties of the energetically lowest-lying (B2O3)n (n = 1,…,8) structures are found using density functional theory and the authors’ multistage hierarchical procedure customized for global optimization of quite large cluster structures. With these data and based on the physically consistent scaling regularities for the principal cluster properties, the size-selected thermodynamic functions of boron oxide particles in the gas phase, such as enthalpy, entropy, and specific heat capacity, are derived. The variation of these characteristics with increasing cluster size is discussed in detail as well. To facilitate handling of the temperature and size dependences we have found here in further chemical kinetic and equilibrium modeling, the tabulated thermodynamic functions of interest are fitted for n = 1,…,1000 to the standard seven-parameter Chemkin polynomials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...