Quaternary ammonium substituted pullulan accelerates wound healing and disinfects Staphylococcus aureus infected wounds in mouse through an atypical ‘non-pore forming’ pathway of bacterial membrane disruption†
Abstract
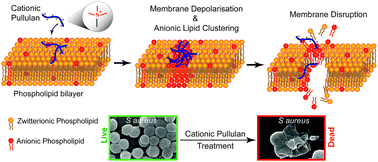
The emergence of multi-drug resistant pathogens has fueled the search for alternatives to the existing line of antibiotics that can eradicate pathogens without inducing resistance development. Here, we report the accelerated wound healing and disinfection potential of a non-amphiphilic quaternized fungal exopolysaccharide, pullulan, without resistance generation in pathogens. The quaternary ammonium substituted pullulan (CP) derivatives showed excellent bactericidal activity against both Gram negative (MBC90 = 1.5 μg mL−1) and Gram positive (MBC90 = 0.25 μg mL−1) bacteria at very low concentrations without showing any toxicity towards mammalian cells. A combined approach of atomistic molecular dynamics simulation and experimental assays revealed that CP exerts a membrane directed bactericidal action through an atypical “non-pore forming” pathway which is not yet established for any known antibacterial polysaccharides. This involves an increase in membrane roughness, disorder among anionic lipid tails, formation of localized anionic lipid clusters and membrane depolarization, finally leading to physical disruption of the membrane integrity. Moreover, CP also displayed biofilm eradication abilities and emerged as an excellent therapeutic material for disinfection and healing of infected wounds. The present work shows the potential of exploiting polysaccharides as next-generation broad-spectrum antimicrobials and provides a platform for further development of rationally designed pullulan-based functional materials for biomedical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...