Development of a fluorescent test strip sensor based on surface positively-charged magnetic bead separation for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
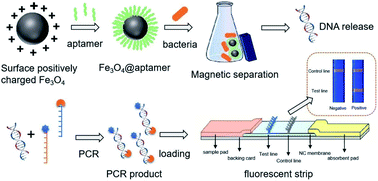
Listeria monocytogenes is one of the major foodborne pathogens, which may cause serious food safety problems and illnesses in humans and animals. Consequently, sensitive, fast and reliable detection methods, as well as effective sample preparation methods are in great demand. In this study, a magnetic separation method based on a aptamer functionalized positively-charged magnetic beads (Fe3O4@aptamer) was established and a fluorescent test strip sensor was constructed for the rapid, sensitive and specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Benefiting from the dual recognition and signal amplification process of Fe3O4@aptamer enrichment and the polymerase chain reaction of the hly gene, the fluorescent strip sensor for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes was determined to be reliable and sensitive, with a linear curve obtained in the range of 1.0 × 102 to 1.9 × 108 CFU mL−1, and a detection limit of 1.0 × 102 CFU mL−1. The detection was achieved in 3 h without culture enrichment. Furthermore, the developed method was successfully applied for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes in pork tenderloin, with the recoveries ranging from 91.1% to 97.1%, and a coefficient of variation of less than 23.4%, revealing the feasible and reliable application of this method in practical samples. The proposed fluorescent strip sensor is rapid, sensitive and specific, giving it great application prospects for use in the field of pathogenic bacterium detection.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...