Profiling of branched-chain fatty acids via nitroxide radical-directed dissociation integrated on an LC-MS/MS workflow†
Abstract
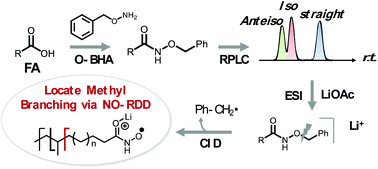
Chain modifications on fatty acyls, such as methyl branching, are important to modulate the biochemical and biophysical properties of lipids. The current lipid analysis workflows which mainly rely on collisional-induced dissociation (CID) to obtain the structural information of lipids often fail in locating the chain modifications. Radical-directed dissociation (RDD) is a new type of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) method capable of producing intrachain cleavages, thus allowing the detailed characterization of lipid structures. In this study, we have developed an RDD method induced by nitroxide radicals (NO˙) for the analysis of branched-chain fatty acids (BCFAs). Fatty acids (FAs) are first amidated by O-benzylhydroxylamine; MS2 CID of the lithium adduct ion of the derivatized FAs uncages the nitroxide radical, which subsequently initiates RDD along the chain. The location of methyl branching can be determined via characteristic 28 Da spacing due to cleavages on either side of the branching point, with enhanced fragmentation observed toward the carbonyl end. This nitroxide-RDD method has been integrated onto reversed-phase liquid chromatography and applied for the profiling of BCFAs from yak milk powder and pooled human plasma samples. Other than the more often encountered iso- and anteiso-BCFAs, we have identified FA n-5 17 : 0 as a minor component from human plasma, which has been rarely reported before.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...