A controllable staining colorimetric method based on carboxylated cellulose membranes for early-warning and semi-quantitative detection of aflatoxins in water
Abstract
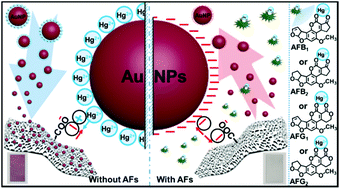
The group specific assay of total aflatoxins (AFs) often requires specific antibodies. A controllable staining colorimetric method was proposed to determine AFs by exploiting controllable electrostatic-staining of carboxylated cellulose membranes (CCMs) with Hg2+-capped gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Under electrostatic force, Hg2+ connects AuNPs and CCMs like a bridge, causing CCMs to be stained by AuNPs. The two adjacent carbonyl groups in the AF structure can chelate Hg2+. When AFs are present, Hg2+ and AFs will form complexes, which reduces the attachment of AuNPs on the CCMs. Therefore, the different degrees of electrostatic-staining of CCMs show different color changes. Based on this phenomenon, a naked-eye colorimetric detection assay of AFs was designed. The visual limit of detection (VLOD) reached 10 ppb, which makes it easily and effectively complete the early-warning and semi-quantitative detection of AFs. To our knowledge, this is the first method for colorimetric detection of AFs based on the controllable electrostatic-staining mechanism, which can be used for the determination of AFs in actual water samples such as beer and beverages. Besides, the colorimetric sensing method based on the controllable electrostatic-staining mechanism provides a novel methodology for early-warning and semi-quantitative detection of toxic and hazardous substances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...