Non-enzymatic electrochemical determination of salivary cortisol using ZnO-graphene nanocomposites†
Abstract
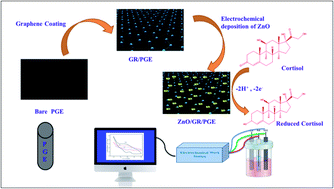
Electrochemically deposited ZnO nanoparticles on a pencil graphite electrode (PGE) coated with graphene generate a noteworthy conductive and selective electrochemical sensing electrode for the estimation of cortisol. Electrochemical techniques such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopic (EIS) tests were adopted to analyze and understand the nature of the modified sensor. Surface morphological analysis was done using various spectroscopic and microscopic techniques like X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Structural characterization was conducted by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The effect of scan rate, concentration, and cycle numbers was optimized and reported. Differential pulse voltammetric (DPV) analysis reveals that the linear range for the detection of cortisol is 5 × 10−10M − 115 × 10−10 M with a very low-level limit of detection value (0.15 nM). The demonstrated methodology has been excellently functional for the determination of salivary cortisol non-enzymatically at low-level concentration with enhanced selectivity despite the presence of interfering substances.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...