Solvent-assisted delamination of layered copper dithienothiophene-dicarboxylate (DUT-134)†
Abstract
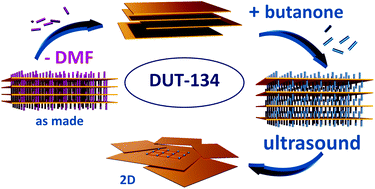
The isolation of 2D nanosheets of layered metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) has become an active research field due to the various advantages resulting from shape anisotropy. The most sophisticated method to obtain the nanostructures of interest is the top-down approach using an external physical energy input, such as ultrasound. In the present work, we rationalize the choice of solvent most suitable for the delamination of the bulk crystals of paddle wheel-based layered MOF [Cu2(dttc)2]n (DUT-134(Cu); dttc: dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]thiophene-2,6-dicarboxylate) as a model system, containing a bent organic linker. The ideal delamination solvent can tear the layers apart and prevent the agglomeration of nanosheets in suspension. The impact of different guest molecules, such as alcohols and ketones on the MOF structure, was studied by analyzing the single-crystal structures of the respective compounds and the behavior of desolvated MOF upon the physisorption of corresponding guests. In situ experiments facilitated the understanding of the adsorption process and structural transition in this layered structure. The most suitable solvents to delaminate DUT-134(Cu) turned out to be ketones, particularly acetone and butanone, giving a stable suspension of ∼10 nm-thick nanosheets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...