A sustainable chemical process to recycle end-of-life silicon solar cells†
Abstract
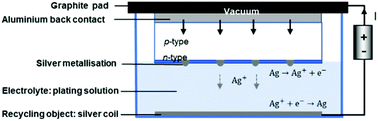
The proper disposal of photovoltaic modules has become an emerging environmental and social issue as modules installed around the 2000s have started entering their end-of-life stage. The decommissioning volume will keep increasing, reaching the gigawatt scale, or millions of tons, by 2030. End-of-life silicon photovoltaic modules contain various valuable materials, such as high-purity silicon and silver. Recycling silicon and silver from the end-of-life modules can significantly improve the recycling revenue. We developed an environmentally sustainable chemical process for simultaneously recovering high-purity silver and silicon from waste solar cells in a fast, efficient, and environmentally friendly way. Reverse electroplating with a full-area contact can successfully recover 99.9% purity metallic silver with a 95% yield within a few minutes. The electrolyte can be reused. The applied voltage and current densities play an important role in achieving a high recycling yield. Subsequent alkaline etching can recover 4N purity silicon with a 99% yield. The chemical process minimises chemical consumption and waste disposal, resulting in the avoidance of 1.60 kg CO2-eq Climate Change impact per kg cell recycled. Even though further chemical etching can remove impurities from the silicon surface to recover up to 5N silicon, the use of strong acids involves serious environmental disadvantages, the overall impacts of which are much higher than those of recovering 4N silicon using a simplified chemical process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...