Chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoformulation carrying paraquat: insights on its enhanced herbicidal activity†
Abstract
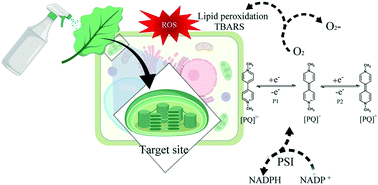
Despite the wide range of possible applications of nanopesticides, the mechanisms involved in their enhanced action remain largely unknown. Understanding the interaction between nanopesticides and plants is crucial for evaluating their potential safety application. Using an experimental and theoretical approach, this study aimed to investigate the target effect of paraquat-loaded chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles (ca. 200 nm) on photosystem I (PSI). Electrochemical analysis showed distinct electroactivity behaviour between the encapsulated and non-encapsulated herbicide. The amount of lipid peroxidation, photooxidizable P700 reaction centre content, and NADPH/NADP+ ratio levels were significantly decreased in spinach leaf tissue exposed to the nanoherbicide compared to those with the non-encapsulated herbicide. The data also revealed that the nanoformulation might promote oxidative stress based on changes observed in antioxidant enzymes. Also, molecular docking results showed a preferential disposition of the herbicide paraquat and paraquat–tripolyphosphate complex (TPP:PQ) in the ligand domain close to FAD and Glu312. Due to the inhibitor's strategic position in the catalytic pocket, a model of electron-capture is proposed, where the herbicide disturbs the redox process NADP+ ⇌ NADPH by capturing electrons to reduce itself. Finally, our findings provide important insights where the redox behaviour of paraquat may play a key role in the enhanced efficiency of nanoherbicides to the target binding site.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...