Heterolytic cleavage of dihydrogen (HCD) in metal nanoparticle catalysis†
Abstract
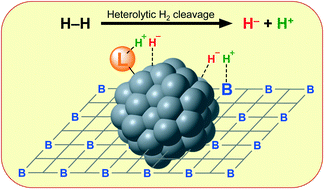
The heterolytic cleavage of H2 into H+ and H−, and the subsequent transfer of these hydrogen species to polarized C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) X groups, is a useful strategy to obtain high selectivities in catalytic hydrogenation reactions, which are one of the most important chemical processes. In the homogeneous field, this transformation is catalyzed by a wide variety of metal–ligand complexes, leading to the selective reduction of ketones, aldehydes, and imines, to name a few. In many cases, a ligand–metal cooperative mechanism promotes the activation of the hydrogen molecule; that is, a Lewis basic site of the ligand binds the proton, and simultaneously, a coordinated metal atom acts as a Lewis acid and takes the hydride. Similar to homogeneous catalysts based on organometallic complexes, in the field of metal nanoparticle catalysis the use of supports, ligands and additives can promote heterolytic H2 splitting by a cooperative mechanism with the metal, and thus produce the selective reduction of thermodynamically more stable unsaturated groups. This successful approach has allowed very high selectivities to be obtained, with both supported and non-supported metal nanoparticles (MNPs). This Perspective aims to carry out a critical review of recent examples on heterolytic cleavage of dihydrogen mediated by MNPs, making a selection of the most representative works in search for general features and new steps to be followed. As will be shown, promising advances have been made through the use of supported MNPs functionalized by organic ligands, which combine the advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts (activity, selectivity, stability and recyclability), and thus represent a new research area with tremendous industrial interest.
X groups, is a useful strategy to obtain high selectivities in catalytic hydrogenation reactions, which are one of the most important chemical processes. In the homogeneous field, this transformation is catalyzed by a wide variety of metal–ligand complexes, leading to the selective reduction of ketones, aldehydes, and imines, to name a few. In many cases, a ligand–metal cooperative mechanism promotes the activation of the hydrogen molecule; that is, a Lewis basic site of the ligand binds the proton, and simultaneously, a coordinated metal atom acts as a Lewis acid and takes the hydride. Similar to homogeneous catalysts based on organometallic complexes, in the field of metal nanoparticle catalysis the use of supports, ligands and additives can promote heterolytic H2 splitting by a cooperative mechanism with the metal, and thus produce the selective reduction of thermodynamically more stable unsaturated groups. This successful approach has allowed very high selectivities to be obtained, with both supported and non-supported metal nanoparticles (MNPs). This Perspective aims to carry out a critical review of recent examples on heterolytic cleavage of dihydrogen mediated by MNPs, making a selection of the most representative works in search for general features and new steps to be followed. As will be shown, promising advances have been made through the use of supported MNPs functionalized by organic ligands, which combine the advantages of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts (activity, selectivity, stability and recyclability), and thus represent a new research area with tremendous industrial interest.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...