Resolving hepatic fibrosis via suppressing oxidative stress and an inflammatory response using a novel hyaluronic acid modified nanocomplex†
Abstract
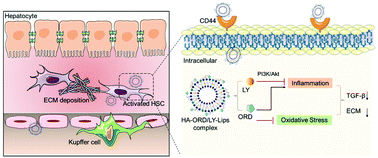
Hepatic fibrosis remains a serious threat to human health globally and there are no effective antifibrotic pharmacotherapeutic strategies, to date. Upon the activation of hepatic stellate cells, excess deposition of the extracellular matrix occurs, acting as a trigger that generates reactive oxygen species and an inflammatory response, thereby exacerbating the development of hepatic fibrosis and inflammation. In this study, we incorporated an idea that targets key pathways for developing novel anti-fibrosis nanomedicine. Previous studies have reported the potential of LY294002 (LY) as a PI3K/Akt inhibitor that suppresses the HSC activation and fibrosis development; however, its poor water solubility impedes further investigation. Moreover, the proliferation of HSC, severe oxidative stress and inflammatory conditions could be undermined by oridonin (ORD) treatment. Herein, we developed an HA-ORD/LY-Lips nanocomplex, where LY294002 was encapsulated into liposomes to prepare LY-Lips while ORD was conjugated with a hyaluronic acid (HA) polymer acting as a prodrug HA-ORD. The complex exerts great potential in improving the liver-targeted drug release. We adopted a series of in vitro and in vivo evaluations which demonstrate that HA-ORD/LY-Lips can significantly avert activation of hepatic stellate cells via scavenging reactive oxygen species and suppressing an inflammatory response. Our work implements a proof of concept strategy for fibrosis treatment based on the dual antioxidative and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, which may be applicable to treat liver fibrosis associated with a dysregulated inflammatory microenvironment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...