Intrinsically radiopaque and antimicrobial cellulose based surgical sutures from mechanically powerful Agave sisalana plant leaf fibers†
Abstract
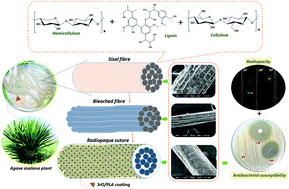
The judicious configuration of a flexible radiopaque suture would be exemplary to facilitate effortless tracking and precise diagnosis of the sutured surgical site by various X-ray assisted imaging modalities and simultaneously serve as a complementary tool for monitoring the fate of the suture material during the post-operative course. A unique radiopaque cellulose based surgical suture (RF) with good mechanical properties was developed by strategically controlled mercerization and bleaching of mechanically strong natural cellulosic fibers extracted from Agave sisalana plant leaves followed by the facile dip-coating of SrO integrated polylactic acid (PLA). RF exhibited admirable straight-pull tensile strength (184 MPa) and commendable contrast enhancement (277.4%) under digital X-ray radiographic imaging which was further validated by micro-CT analysis. Further, RF has a controlled hydrolytic degradation profile favorable for surgical suturing (mass loss ∼22% in 28 days). The microporous surface architecture of RF (pore size < 10 μm) as a result of SrO–PLA coating enabled the loading of antibiotic (ciprofloxacin) deep inside the pores with a cumulative release of 24% at 28 days under physiological conditions substantiating its feasibility to be used as an efficient antimicrobial suture (CRF) that prevents possible bacterial infections at the surgical site. This has been demonstrated by antibacterial disc diffusion assay performed against two Gram-positive and two Gram-negative bacterial strains. Significantly, both RF and CRF are highly biocompatible as confirmed by MTT assay and F-actin staining. Hence, CRF would be a good biocompatible suture candidate holding good tensile properties, exceptional antimicrobial property and intrinsic radiopacity retention for a period >28 days.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...