SPECT imaging and highly efficient therapy of rheumatoid arthritis based on hyperbranched semiconducting polymer nanoparticles†
Abstract
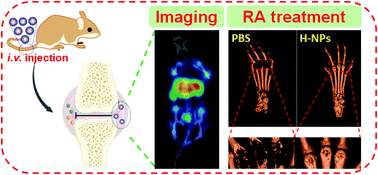
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory autoimmune disease. Although significant progress has been made in clinical treatment, joint inflammation may continue or worsen, and may even progress to the end-stage that requires joint replacement. Traditional therapy using methotrexate (MTX) would cause serious off-target systemic toxicities. Therefore, it is crucial to effectively and specifically deliver MTX to targeted inflamed joints to decrease its adverse systemic toxicities and improve its therapeutic index. Herein, we develop multifunctional nanocarriers for diagnostic radioisotope (99mTc) labeling and therapeutic targeted drug (MTX) delivery by using PEGylated hyperbranched semiconducting polymer nanoparticles (HSP-PEG-NPs) as carriers. Upon intravenous administration, the nanoparticles can extravasate through the turbulent blood–joint barrier and access the inflamed joints. In vivo SPECT/CT imaging shows high accumulation in the inflamed joints of mice with RA after intravenous injection of HSP-PEG-NPs with 99mTc labeling (99mTc-HSP-PEG). In vivo therapeutic evaluations suggest that MTX@HSP-PEG-NPs significantly alleviate RA with a high therapeutic index and relatively low adverse systemic toxicities in comparison with free MTX at the same dose. Our study shows that HSP-PEG-NPs could serve as multifunctional vehicles to deliver radioisotopes for in vivo imaging, and MTX for RA treatment, highlighting the innovative development of the nanoparticle-based RA treatment strategy for clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...