Bifunctional scaffolds of hydroxyapatite/poly(dopamine)/carboxymethyl chitosan with osteogenesis and anti-osteosarcoma effect†
Abstract
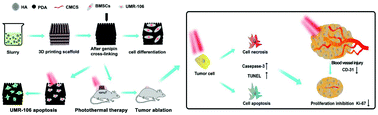
The bifunctional tissue engineering scaffold with anti-tumor and bone repair properties is promising for the therapy of bone tumor where large bone defects often occur. In this study, hydroxyapatite (HA), poly(dopamine) (PDA), and carboxymethyl chitosan (CMCS) composite scaffolds were prepared by the 3D-printing technology. PDA significantly improved the rheological properties of the slurry for molding, mechanical properties, surface relative potential, and water absorption of composite scaffolds. The osteogenic properties of HA/PDA/CMCS composite scaffolds were evaluated by the cell experiment in vitro. The photothermal properties and anti-tumor effects of the scaffolds in vivo were assessed by the tumor model in nude mice. HA/PDA/CMCS composite scaffolds could promote more osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow stromal cells (mBMSCs) than scaffolds without PDA in vitro and the effect was not hindered by the photothermal process. The PDA-modified composite scaffold had excellent photothermal properties. Cell experiments showed that scaffolds with PDA under irradiation could suppress the tumor effectively. In vivo anti-tumor effects in nude mice indicated that the HA/PDA/CMCS composite scaffold promoted cell apoptosis/necrosis by the direct photothermal effect. Vascular injury was developed subsequently, which lead to the suppression of tumor cell proliferation due to hypoxia-ischemia. HA/PDA/CMCS composite scaffolds with multiple effects have great potential application in bone tumor therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...