A library of aminoglycoside-derived lipopolymer nanoparticles for delivery of small molecules and nucleic acids†
Abstract
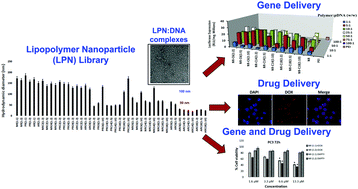
Simultaneous delivery of small molecules and nucleic acids using a single vehicle can lead to novel combination treatments and multifunctional carriers for a variety of diseases. In this study, we report a novel library of aminoglycoside-derived lipopolymers nanoparticles (LPNs) for the simultaneous delivery of different molecular cargoes including nucleic acids and small-molecules. The LPN library was screened for transgene expression efficacy following delivery of plasmid DNA, and lead LPNs that showed high transgene expression efficacies were characterized using hydrodynamic size, zeta potential, 1H NMR and FT-IR spectroscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. LPNs demonstrated significantly higher efficacies for transgene expression than 25 kDa polyethyleneamine (PEI) and lipofectamine, including in presence of serum. Self-assembly of these cationic lipopolymers into nanoparticles also facilitated the delivery of small molecule drugs (e.g. doxorubicin) to cancer cells. LPNs were also employed for the simultaneous delivery of the small-molecule histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor AR-42 together with plasmid DNA to cancer cells as a combination treatment approach for enhancing transgene expression. Taken together, our results indicate that aminoglycoside-derived LPNs are attractive vehicles for simultaneous delivery of imaging agents or chemotherapeutic drugs together with nucleic acids for different applications in medicine and biotechnology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
