Formation and characterization of crosslinks, including Tyr–Trp species, on one electron oxidation of free Tyr and Trp residues by carbonate radical anion†
Abstract
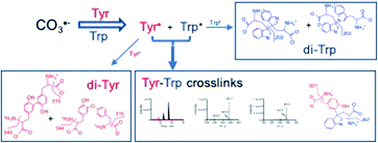
Dityrosine and ditryptophan bonds have been implied in protein crosslinking. This is associated with oxidative stress conditions including those involved in neurodegenerative pathologies and age-related processes. Formation of dityrosine and ditryptophan derives from radical–radical reactions involving Tyr˙ and Trp˙ radicals. However, cross reactions of Tyr˙ and Trp˙ leading to Tyr–Trp crosslinks and their biological consequences have been less explored. In the present work we hypothesized that exposure of free Tyr and Trp to a high concentration of carbonate anion radicals (CO3˙−), under anaerobic conditions, would result in the formation of Tyr–Trp species, as well as dityrosine and ditryptophan crosslinks. Here we report a simple experimental procedure, employing CO3˙− generated photochemically by illumination of a Co(III) complex at 254 nm, that produces micromolar concentrations of Tyr–Trp crosslinks. Analysis by mass spectrometry of solutions containing only the individual amino acids, and the Co(III) complex, provided evidence for the formation of o,o′-dityrosine and isodityrosine from Tyr, and three ditryptophan dimers from Trp. When mixtures of Tyr and Trp were illuminated in an identical manner, Tyr–Trp crosslinks were detected together with dityrosine and ditryptophan dimers. These results indicate that there is a balance between the formation of these three classes of crosslinks, which is dependent on the Tyr and Trp concentrations. The methods reported here allow the generation of significant yields of isolated Tyr–Trp adducts and their characterization. This technology should facilitate the detection, and examination of the biological consequences of Tyr–Trp crosslink formation in complex systems in future investigations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...