Self-assembled functional components-doped conductive polypyrrole composite hydrogels with enhanced electrochemical performances
Abstract
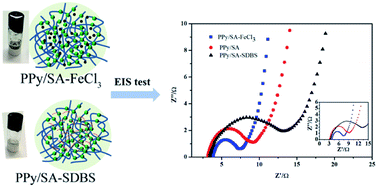
A conductive hydrogel is a composite conductive material formed by combining a conductive polymer with a nanogel structure of a hydrogel. Conductive hydrogels not only have potential applications in supercapacitors, sensors, and modulators, they can also be synthesized by many methods, such as copolymerization, crosslinking, and grafting. In this work, we successfully prepared three conductive composite hydrogels by in situ polymerization, namely polypyrrole sodium alginate conductive hydrogel, ferric chloride-doped polypyrrole sodium alginate hydrogel and doped polypyrrole sodium alginate hydrogel with sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate. In addition, a series of characterizations were performed for the three conductive hydrogels described above. The results show that the polypyrrole sodium alginate hydrogel doped with ferric chloride forms a nanofiber network with a more stable structure and better electrochemical performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...