Design of configuration-restricted triazolylated β-d-ribofuranosides: a unique family of crescent-shaped RNase A inhibitors†
Abstract
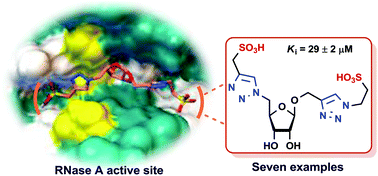
Seven new carbohydrate–bistriazole hybrid molecules were designed taking into consideration the crescent shaped active site of ribonuclease A (RNase A). In this case, the β-D-ribofuranose structure was used as the basic building unit; both the C1 and C4 arms protruding out towards the β-face of the tetrahydrofuran moiety of the ribose sugar provided an overall “U” shape to the basic building block. Several combinations of bistriazole moieties were constructed on the two arms of this basic building block. These mono- and/or bis-substituted 1,2,3-triazole units were linked to acidic functional groups because of the overall basic nature of the hydrolytic site of RNase A. All these compounds were efficient competitive inhibitors of RNase A with inhibition constants (Ki) in the micromolar range. In contrast to the carboxylic acid-modified hybrid molecules, molecules carrying sulfonic acids were found to be more potent because of the stronger interactions with the positively charged active site. The most efficient inhibitor of the series was the disulfonic acid-functionalized carbohydrate-bis-triazole hybrid molecule. Docking studies disclosed that the molecule, because of its well defined “U” shape with flexible arms, fits effectively in the active site; moreover, in all cases, besides the acid groups, the triazole and sugar rings also actively participated in creating the hydrogen bonding network in the cavity of the enzyme active site.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Chemical Biology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...