iDHS-DASTS: identifying DNase I hypersensitive sites based on LASSO and stacking learning†
Abstract
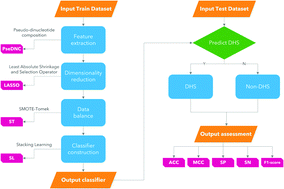
The DNase I hypersensitivity site is an important marker of the DNA regulatory region, and its identification in the DNA sequence is of great significance for biomedical research. However, traditional identification methods are extremely time-consuming and can not obtain an accurate result. In this paper, we proposed a predictor called iDHS-DASTS to identify the DHS based on benchmark datasets. First, we adopt a feature extraction method called PseDNC which can incorporate the original DNA properties and spatial information of the DNA sequence. Then we use a method called LASSO to reduce the dimensions of the original data. Finally, we utilize stacking learning as a classifier, which includes Adaboost, random forest, gradient boosting, extra trees and SVM. Before we train the classifier, we use SMOTE-Tomek to overcome the imbalance of the datasets. In the experiment, our iDHS-DASTS achieves remarkable performance on three benchmark datasets. We achieve state-of-the-art results with over 92.06%, 91.06% and 90.72% accuracy for datasets ![[Doublestruck S]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e176.gif) 1,
1, ![[Doublestruck S]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e176.gif) 2 and
2 and ![[Doublestruck S]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e176.gif) 3, respectively. To verify the validation and transferability of our model, we establish another independent dataset
3, respectively. To verify the validation and transferability of our model, we establish another independent dataset ![[Doublestruck S]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e176.gif) 4, for which the accuracy can reach 90.31%. Furthermore, we used the proposed model to construct a user friendly web server called iDHS-DASTS, which is available at http://www.xdu-duan.cn/.
4, for which the accuracy can reach 90.31%. Furthermore, we used the proposed model to construct a user friendly web server called iDHS-DASTS, which is available at http://www.xdu-duan.cn/.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...