In situ processed tungsten carbide/carbon black-supported platinum electrocatalysts for enhanced electrochemical stability and activity†
Abstract
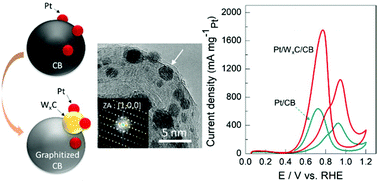
High performance electrocatalysts have been intensively studied to reduce the usage of expensive platinum-group metals and to obtain excellent electrochemical durability. Herein, we introduce a very promising processing technique based on the low-temperature in situ synthesis of tungsten carbide nanoparticles with carbon under a highly energetic arc plasma atmosphere prior to the deposition of Pt nanoparticles. There is no external supply of carbon for this synthesis since the carbon black (CB) support acts as a source of carbon. Multiple phases, including WC, W2C, and W1−xC, were found to exist by the electron diffraction analytical simulation technique. The final structure of Pt/WxC/CB showed significantly better performance in terms of electrocatalytic activities, such as electrochemically active surface area, methanol oxidation activity, mass activity, CO tolerance, and 10 000 cycle-accelerated durability test, compared to those of the commercial reference sample containing more Pt. The origin of the enhancement was understood to be associated primarily with the presence of WxC itself, a smaller scale of well dispersed WxC nanoparticles, reduced oxidation of Pt, and graphitization of the CB matrix.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...