An in-depth study of Sn substitution in Li-rich/Mn-rich NMC as a cathode material for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
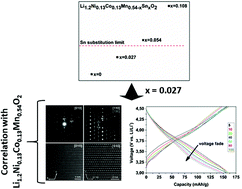
Layered Li-rich/Mn-rich NMC (LMR-NMC) is characterized by high initial specific capacities of more than 250 mA h g−1, lower cost due to a lower Co content and higher thermal stability than LiCoO2. However, its commercialisation is currently still hampered by significant voltage fade, which is caused by irreversible transition metal ion migration to emptied Li positions via tetrahedral interstices upon electrochemical cycling. This structural change is strongly correlated with anionic redox chemistry of the oxygen sublattice and has a detrimental effect on electrochemical performance. In a fully charged state, up to 4.8 V vs. Li/Li+, Mn4+ is prone to migrate to the Li layer. The replacement of Mn4+ for an isovalent cation such as Sn4+ which does not tend to adopt tetrahedral coordination and shows a higher metal–oxygen bond strength is considered to be a viable strategy to stabilize the layered structure upon extended electrochemical cycling, hereby decreasing voltage fade. The influence of Sn4+ on the voltage fade in partially charged LMR-NMC is not yet reported in the literature, and therefore, we have investigated the structure and the corresponding electrochemical properties of LMR-NMC with different Sn concentrations. We determined the substitution limit of Sn4+ in Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54−xSnxO2 by powder X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy to be x ≈ 0.045. The limited solubility of Sn is subsequently confirmed by density functional theory calculations. Voltage fade for x = 0 and x = 0.027 has been comparatively assessed within the 3.00 V–4.55 V (vs. Li/Li+) potential window, from which it is concluded that replacing Mn4+ by Sn4+ cannot be considered as a viable strategy to inhibit voltage fade within this window, at least with the given restricted doping level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...