Molecular evolution pathways during nucleation of small organic molecules: solute-rich pre-nucleation species enable control over the nucleation process†
Abstract
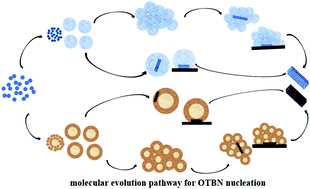
Increasing evidence has shown that nucleation pathways involving disordered pre-nucleation species exist in the nucleation process of many types of solid state products, especially inorganic solid state products. Studying the thermodynamic and kinetic properties of these pre-nucleation species is crucial to understand and control the nucleation process of solid state products. In this work, the evolution pathway of molecular or supramolecular structures during the nucleation process was investigated by using 2-cyano-4′-methylbiphenyl (OTBN) as a model compound. In the resultant solutions, similar pre-nucleation clusters were analyzed and characterized by dynamic light scattering (DLS), small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). It was found that the clusters were disordered and liquid-like and did not represent any of the known OTBN condensed phases. They were of interest since they may be the key sites for the formation of new crystal nuclei of OTBN. It was demonstrated that the change in the solvation effect would drive the pre-nucleation clusters to exhibit very different structures. How the clusters vary with concentration and temperature, and how they differ before and after nucleation have been systematically studied. In addition, the molecular dynamics of the evolution of clusters, the effect of initial mixing process on clusters and the nucleation dynamics were also investigated. The results suggested that the pre-nucleation clusters played a key role in the process of crystallization of organic small molecules, indicating that the dynamics of nucleation could be regulated by changing the structure and size of the pre-nulceation clusters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...