Bioinspired β-glucan microcapsules deliver FK506 to lymph nodes for treatment of cardiac allograft acute rejection†
Abstract
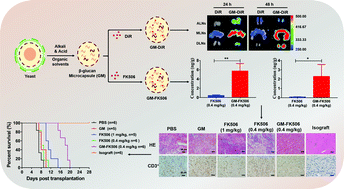
Lymph node (LN)-targeted delivery exhibits enormous potential to improve the treatment efficacy of immunosuppressants for transplantation. However, current strategies are still limited by the inefficiency of delivery by passive targeting, the high cost of antibody-mediated active targeting, as well as poor patient compliance by parenteral delivery. Herein, bioinspired β-glucan microcapsules (GM) was used to load and transfer low dose FK506 into LNs via oral administration, which may relieve cardiac allograft acute rejection with low nephrotoxicity. The LN distribution study showed that both DiR and FK506 were delivered into the LNs effectively via GM-mediated transport after 24 h and were present in the LNs for at least 48 h. The FK506-loaded GM (GM-FK506) significantly prolonged allograft survival compared with the PBS group (mean survival time, 17.8 ± 1.9 versus 7.3 ± 1.0 days; P < 0.01), and marked decreased the acute rejection grade. Furthermore, T cell infiltration, and secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ were dramatically reduced in the GM-FK506 group. As expected, no nephrotoxicity was observed after five consecutive administrations of GM-FK506. Our results demonstrate that GM-FK506 is a promising strategy for the treatment of cardiac allograft acute rejection, indicating that GM mediated LNs targeting may provide a potential opportunity for managing immune-related diseases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...