Mechanistic control of a galvanic replacement reaction on cuprous oxide†
Abstract
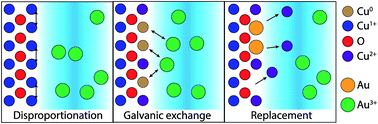
Galvanic replacement (GR) reactions are a versatile approach to fabricating hierarchically structured functional nanomaterials for catalytic, plasmonic, and sensing applications. Most research efforts aim to identify chemical strategies to control the resultant morphology of GR deposition on metallic nanoparticle seeds. Recently, GR has become a method of interest for fabricating heterogeneous interfaces for these applications. Here, we study the chemical mechanism for the GR reaction of AuCl4− on Cu-based thin films. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and structural characterization show that, while the GR reaction proceeds through the direct dissolution of Cu and reduction of AuCl4− on Cu, the reaction on Cu2O results in the solid-state formation of CuO at the interface which passivates the interface from further Au deposition. As a result, the chemistry and morphology of Au deposited on Cu2O is limited by the rate of CuO dissolution in the background acidic electrolyte. To explain the observed differences between the GR reaction of AuCl4− on Cu and Cu2O interfaces, we propose a new mechanism for the GR reaction on Cu2O surfaces where disproportionation is the limiting intermediate reaction which can be mediated by AuCl4− concentration and by the photoelectrochemical generation of Cu nanoparticles throughout the bulk of the Cu2O. Consequently, the hierarchical structure of the GR deposition of Au can be chemically controlled on Cu2O films. More generally, this highlights how the details of the chemical kinetics at the reaction interface can be exploited to tailor the resulting nanostructure of metals deposited via GR reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...