Charge injection and transport properties of large area organic junctions based on aryl thin films covalently attached to a multilayer graphene electrode
Abstract
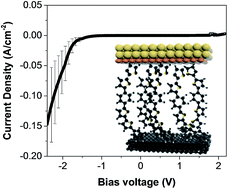
The quantum interaction between molecules and electrode materials at molecule/electrode interfaces is a major ingredient in the electron transport properties of organic junctions. Driven by the coupling strength between the two materials, it results mainly in the broadening and energy shift of the interacting molecular orbitals. Using new electrode materials, such as the recently developed semi-conducting two-dimensional nanomaterials, has become a significant advancement in the field of molecular/organic electronics that opens new possibilities for controlling the interfacial electronic properties and thus the charge injection properties. In this article, we report the use of atomically thin two-dimensional multilayer graphene films as the base electrode in organic junctions with a vertical architecture. The interfacial electronic structure dominated by the covalent bonding between bis-thienyl benzene diazonium-based molecules and the multilayer graphene electrode has been probed by ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy and the results are compared with those obtained on junctions with standard Au electrodes. Room temperature injection properties of such interfaces have also been explored by electron transport measurements. We find that, despite strong variations of the density of states, the Fermi energy and the injection barriers, both organic junctions with Au base electrodes and multilayer graphene base electrodes show similar electronic responses. We explain this observation by the strong orbital coupling occurring at the bottom electrode/bis-thienyl benzene molecule interface and by the pinning of the hybridized molecular orbitals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...