Photothermal-modulated reversible volume transition of wireless hydrogels embedded with redox-responsive carbon dots†
Abstract
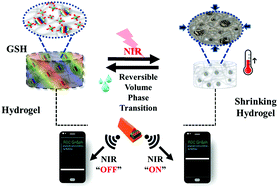
The reversible volume transition of redox-responsive hydrogels by near-infrared (NIR) irradiation has recently attracted significant attention as a novel therapy matrix for tracking and treating cancer via stimuli-responsive fluorescence on/off with controllable volume transition via a wireless sensing system. Herein, a NIR-induced redox-sensitive hydrogel was synthesized by blending a hydrogel with IR825-loaded carbon dots (CD) to achieve enhanced mobility of nanoparticles inside a gel network, and reversible volume phase transitions remotely controlled by a smartphone application via the induction of different redox environments. The presence of CD-IR825 in the thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel network imparted fluorescence, electronic and photothermal properties to the hydrogels, which resulted in volume shrinkage behavior of the hydrogel upon exposure to NIR laser irradiation due to the redox-sensitive CDs. Under the NIR on/off cycles, the photothermal temperature, fluorescence, and porous structure were reversed after turning off the NIR laser. The hydrogel responsiveness under GSH and NIR light was studied using a wireless device based on the changes in the resistance graph on a smartphone application, generating a fast and simple method for the investigation of hydrogel properties. The in vitro cell viabilities of the MDA-MB cancer cells incubated with the composite hydrogel in the presence of external GSH exhibited a higher photothermal temperature, and the cancer cells were effectively killed after the NIR irradiation. Therefore, the NIR-induced redox-responsive nanocomposite hydrogel prepared herein has potential for use in cancer treatment and will enable the study of nanoparticle motion in hydrogel networks under multiple stimuli via a wireless device using a faster and more convenient method.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...