Development of an antibacterial surface with a self-defensive and pH-responsive function†
Abstract
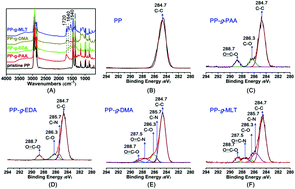
In this work, a charge conversion mechanism was introduced to build a bacteria responsive antibacterial surface. The antimicrobial surface is constructed by immobilizing pH-responsive moieties on the surface of the material, followed by immobilization of the antimicrobial peptide (AMP) melittin (MLT) by strong electrostatic interaction. The constructed surface exhibited self-defensive properties against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. In comparison with previously reported self-defensive systems with side effects of drug resistance, this antibacterial surface prevented the undesirable drug resistance. The bactericidal mechanism of the antibacterial surface is involved in a lytic cell membrane. Once bacteria come into contact with the surface, the bactericidal properties will be triggered on the surface. As bacteria exponentially grow, they accumulate and attach to the surface, which will develop a slightly acidic micro-environment and subsequently activate the pH responsive surface to release MLT to kill bacteria. This study broadened our understanding of the development of antibacterial surfaces and provided new insights for the antibacterial surface to be utilized in industrial, biological and medical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...