Efficient synthesis of amino acid polymers for protein stabilization†
Abstract
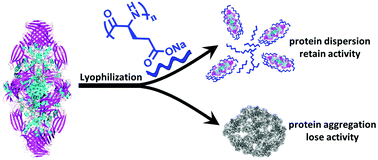
Proteins are fragile such that even freezing, drying and dehydration may induce their denaturation, aggregation, and activity loss. To protect proteins from these kinds of damage, we prepared two types of amino acid polymers, poly-(L-glutamate)-r-poly-(L-lysine) (PLG-r-PLL) and poly-L-glutamate (PLG), from the efficient ring-opening polymerization of α-amino acid N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) using lithium hexamethyldisilazide (LiHMDS) as the initiator. β-galactosidase (β-Gal) was used in this study to examine the protein protecting effect of the synthesized amino acid polymers during lyophilization. The results indicate that both PLG-r-PLL and PLG exert significant protection on β-Gal during lyophilization and improve the activity of the resulting protein from 40%, without using a protecting agent during lyophilization, to 80% of the original protein activity. Nevertheless, PLG generally performs better than PLG-r-PLL independent of the chain length. Our studies also show that PLG and PLG-r-PLL with a high content of PLG subunits display no observable cytotoxicity and hemolytic effect. Furthermore, dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization indicate that PLG protects β-Gal upon lyophilization by preventing the aggregation of β-Gal. Our studies demonstrate that amino acid polymers, such as PLG, can exert potent activity for protein stabilization. The easy operation of LiHMDS-initiated and efficient NCA polymerization implies the great potential of this strategy to prepare amino acid polymers quickly for the screening of protein stabilization and mechanism study.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...