Elucidation of molecular pathways responsible for the accelerated wound healing induced by a novel fibrous chitin dressing
Abstract
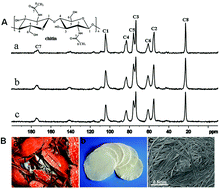
Fibrous chitin dressing (FCD) prepared from a NaOH-urea aqueous solution of chitin via a physical process was used to study its effect on wound healing using a full-thickness cutaneous wound model in rats and mice. It was demonstrated that wounds in rats covered with the FCD showed faster collagen (especially type I collagen) growth and speedier healing than those with Gauze (12 days versus 16 days). The ability of FCD to promote wound healing was also observed on wild-type (WT) mice. For MyD88-knockout mice, however, FCD displayed no beneficial but an adverse effect on wound healing: the healing time for wounds treated with FCD was even longer than those treated with gauze. Importantly, in vivo studies indicated that FCD-treated mice, compared to gauze-treated ones, exhibited markedly higher expressions of MyD88, IKBα, TGF-β, P-TβR II, TβR II and P-Smad2/3 in wild-type mice. For MyD88 knockout mice, however, the expressions of those molecules were inhibited and lowered in FCD-treated ones than those treated with gauze. In vitro studies confirmed that chitin increased the expression of TGF-β, P-TβRII and P-Smad2/3 while the expressions of those molecules were significantly inhibited with CD14 antibody (p < 0.05). These results indicated that FCD accelerated wound healing through a MyD88-dependent pathway, followed by a TGF-β/Smad pathway. This work not only demonstrated the superior wound healing effect of chitin-derived dressing, but also provided for the first time the underlying molecular mechanism, further establishing chitin as an important biomedical material for potential clinical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...