IL-10-secreting human MSCs generated by TALEN gene editing ameliorate liver fibrosis through enhanced anti-fibrotic activity†
Abstract
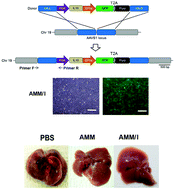
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known for their ability to repair liver damage. However, their therapeutic potential still needs to be enhanced. In the present study, we produced genome-edited MSCs that secrete interleukin 10 (IL-10) and evaluated their therapeutic potential in a liver fibrosis model. Multiple copies of the IL-10 gene were inserted into a safe harbor genomic locus in amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (AMMs) using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). The IL-10 gene-edited AMMs (AMM/I) were characterized by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), and microarray. The effects of AMM/I-conditioned cell medium (CM) on the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) were analyzed in vitro and in vivo therapeutic assays were performed on a mouse liver fibrosis model. The engineered AMM/I expressed high levels of IL-10. AMM/I-CM inhibited the activation of HSC (in vitro) and TNF-α expression of T cells/macrophage derived from fibrotic liver. In addition, human IL-10 was detected in the serum of the mice transplanted with AMM/I and transplantation of AMM/I significantly inhibited thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver fibrosis and ameliorated abnormal liver function. Furthermore, a high number of human albumin-expressing AMM/I were successfully engrafted into the liver of recipient mice. Overall, genome-edited AMMs overexpressing anti-fibrotic IL-10 might be a promising alternative therapeutic option for the treatment of liver cirrhosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...