Cell cycle and transmembrane mitochondrial potential analysis after treatment with chromium(iii), iron(iii), molybdenum(iii) or nickel(ii) and their mixtures
Abstract
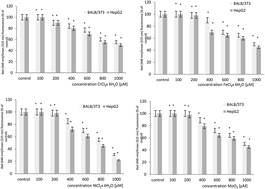
The aim of this study was to examine the effect of chromium(III), iron(III), molybdenum(III) and nickel(II) and their combinations on the cell cycle and mitochondrial transmembrane potential (MTP) in BALB/3T3 and HepG2 cells. A statistically significant dose related decrease of the percentage of cells in the G0/G1 and S phases was observed. However, a statistically significant dose related increase of the percentage of cells in the G2/M phase after exposure to chromium(III), nickel(II) or molybdenum(III) at 200–1000 μM concentrations in both cell lines was observed. Moreover, an increase of the percentage of cells in the subG1 phase was observed. In both cell lines a statistically significant dose related decrease of the percentage of cells in the G2/M phase after exposure to iron(III) at 200–1000 μM concentrations was observed. However, a statistically significant dose related increase of the percentage of cells in the G0/G1 phase after exposure to iron(III) at 200–1000 μM concentrations was observed. A concentration dependent statistically significant decrease in the level of the MTP was observed in both cell lines after exposure to chromium(III), iron(III), nickel(II) and molybdenum(III). The results obtained from both cell lines show that HepG2 cells are more sensitive when compared to BALB/3T3 cells. Additions of Cr(III) at 200 μM plus Fe(III) at 1000 μM showed a synergistic effect on the cell cycle and MTP. In the case of Cr(III) at 200 μM plus Mo(III) at 1000 μM, an antagonistic effect was observed in both analyses. In the case of Cr(III) at 1000 μM plus Mo(III), Ni(II) and Fe(III) at 200 μM, no changes in the percentage of cells in all phases were observed in both cell lines in both analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...