A review of magnesiothermic reduction of silica to porous silicon for lithium-ion battery applications and beyond†
Abstract
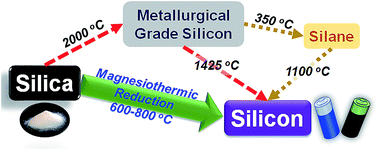
Increasing demands for portable power applications are pushing conventional battery chemistries to their theoretical limits. Silicon has potential as an anode material to increase lithium-ion cell capacity. The associated volume change during lithiation/delithiation leads to a decline in capacity during cycling and low lithium diffusion rates within silicon limit high rate performance. Porous silicon can potentially address the poor cyclability and rate capabilities simultaneously by minimising stresses and providing smaller silicon substructures for lithium diffusion. Template assisted synthesis and magnesiothermic reduction of silica to silicon offers a facile and scalable route for the production of porous silicon structures even when using a non-porous feedstock. This review collates the available literature concerning the effects of reaction conditions through the reduction reaction. We highlight that it is important to report in detail all reaction conditions and complete characterisation of both the reactant and the product. The battery performance of these porous silicon structures is discussed and future research directions are identified. These outcomes will enable the identification of a clear design pathway for the bespoke production of porous silicon.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...