Preparation of a thermally conductive biodegradable cellulose nanofiber/hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheet film: the critical role of edge-hydroxylation
Abstract
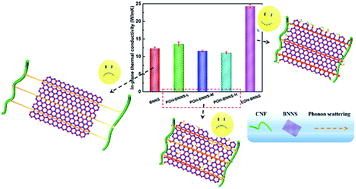
Chemical modification of boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs) is a simple but effective method to improve their dispersion and compatibility within polymer nanocomposites. The key point is how to import compatible functional groups but simultaneously retain the intact crystal lattice. In this study, two different hydroxylation methods, namely nitric acid oxidation and aqueous ball milling, were adopted for surface modification of BNNSs. And a comparative study was carried out in terms of hydroxyl (OH) content, position of modification and the thermal conductivity (TC) after mixing them with a biodegradable cellulose nanofiber (CNF). TEM mapping, XRD and HRTEM indicated that nitric acid oxidation mainly resulted in an in-plane hydroxylation of BNNSs (POH-BNNSs) whose crystal lattice was seriously damaged, while aqueous ball milling led to most likely an edge hydroxylation of BNNSs (EOH-BNNSs) whose crystal lattice could be well preserved. As a result, strikingly, the TC of POH-BNNS filled nanocomposites only showed a little growth (10.2%) at a low OH content or even decreased at a higher OH loading, while an impressive thermal enhancement of almost 100% was achieved for CNF/EOH-BNNS nanocomposites. Such a substantial improvement signifies the critical role of edge-hydroxylation, which can simultaneously reduce interfacial thermal resistance and retain the intact basal crystal lattice to facilitate acoustic phonon transfer. This research provides deep insight into modification of two-dimensional nanomaterials from the point of view of the defect position, and an edge-selective modification strategy is expected to be of great advantage for the fabrication of highly thermally conductive nanocomposites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...